Health Check: does my brain really freeze when I eat ice cream?
It’s a long, hot summer’s day and you’re looking forward to an ice cream. But within seconds of your first bite, you feel a headache coming on: a brain freeze.
What’s going on?
Your brain isn’t literally freezing, or even sensing cold. It can’t sense cold or pain because it lacks its own internal sensory receptors. In fact, surgeons usually perform brain surgery on conscious, sedated patients with the only pain coming from the scalp, skull and underlying tissues, not from the brain itself.
An international team of neurologists classifies brain freeze or ice cream headache as a:
headache attributed to ingestion or inhalation of a cold stimulus.
Anything cold (solid, liquid or gas) that passes over the roof of the mouth (the hard palate) and/or the back of the throat (posterior pharyngeal wall) can trigger a brain freeze headache.
Pain can be to the front of the head or the temples and while short lasting, can be intense, though not debilitating. People who have these headaches usually do not seek treatment, so there has been very little research into how brain freeze occurs.
The transient nature of these headaches means common “treatments”, like putting your tongue on the roof of your mouth, are unlikely to have any major effect.
People most likely to have brain freeze also tend to suffer from migraines, suggesting a common underlying mechanism for both.
One study compared how common brain freeze was in people with migraine alongside those with tension type headaches. When an ice cube was placed on the hard palate of their mouths for 90 seconds, 74% of migraine sufferers reported pain along their temples versus 32% of those with a history of primary headache disorders (headaches that do not have an underlying or identifiable cause).
Only 12% of volunteers without a history of primary headache disorder experienced brain freeze headache with the same stimulus. These observations are robust and have been replicated.
What causes brain freeze?
An old fashioned idea about the cause of migraine suggested excessive blood flow through the blood vessels that supply blood to the brain caused the pain. However, this vascular hypothesis for migraine, although still popular, is now largely discredited.
Just like migraines, brain freeze headaches are accompanied by changes in blood flow through the arteries of the brain. The link between pain associated with altered brain artery blood flow has led some to speculate the blood flow changes may actually cause the pain. But an association between blood flow and pain doesn’t necessarily mean one causes the other.
Another theory about what causes migraine relates to altered excitability of neuronal pathways that detect and transmit the sensation and pain in the head via the trigeminal system, the major nerve that transmits sensory information from the head to the central nervous system.
Ordinarily the cold sensation is not painful. However, if the trigeminal system is prone to over-excitability in people with migraine, pain kicks in at lower level (a lower threshold). If an over-excitable trigeminal system also applies to people with brain freeze, then the threshold may be low enough to activate pain after only a brief exposure to ice cream.
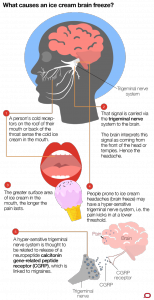
Researchers are studying what causes hyper-excitability of the trigeminal system. The effects of a specific chemical signalling molecule CGRP (calcitonin gene-related peptide) released by trigeminal neurons are a necessary component of migraine pain.
In genetically inherited migraine, the cellular processes that result in the release of CGRP from trigeminal neurons has been altered. These same mechanisms may explain the hypersensitivity to cold stimulus in ice cream headaches.
It seems likely that all headaches are the result of changes in activity in the trigeminal system, although why we perceive them in the front of the head and at the temples in particular is a mystery.
Is there anything I can do to stop brain freeze?
While we do not know exactly what causes brain freeze, there may be a simple way to reduce your chances of having one this summer.
Research shows how long brain freeze headaches last relates to the surface area of the mouth that comes into contact with the cold stimulus. So, if you want to reduce your chance of a brain freeze, you may want to avoid gulping down your ice cream all at once. Take small nibbles instead.
![]() This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.
Share your comments below.





















-

-
-
ChiWren said
- 30 Sep 2024
-

-
-
mom101628 said
- 05 Feb 2017
-

-
-
cherz said
- 01 Feb 2017
-

-
-
robyn_smithwick said
- 24 Jan 2017
-

-
-
june11 said
- 13 Jan 2017
-

-
-
rachelvk said
- 12 Jan 2017
-

-
-
mom93821 said
- 12 Jan 2017
-

-
-
mom81879 said
- 11 Jan 2017
-

-
-
mom112217 said
- 11 Jan 2017
Post a comment10:54 pm
12:08 am
6:52 pm
2:29 pm
7:48 pm
8:56 am
6:45 am
-

-
-
mom93821 replied
- 13 Jan 2017 , 6:39 am
Reply1:08 pm
12:02 pm
To post a review/comment please join us or login so we can allocate your points.